Robotic Inguinal hernia repair is an advancement in the quality of laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair. Laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair was an entirely new approach to groin hernia repair first appearing in the early 90s. It allowed for repairing the hernia from the inside wall or the pelvis through 3 small abdominal incisions. The placement of mesh behind the hernia defect (posterior repair) allowed for better durability and less pain for
inguinal hernia repair.
Now the use of the Intuitive Davinci Robot enables posterior repair with robotic precision. The surgeon's visual resolution is dramatically improved with 3D ultrahigh definition. The surgeon is able to sit down and has much less physical stress than laparoscopy which involves standing and tiring upper extremity movements. Robotic instruments are far more precise and allow for much smoother delicate maneuvers by the surgeon.
Robotic inguinal hernia repair ultimately is a similar, but a more precise technique compared to laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair.
Steps for robotic inguinal hernia repair after the patient is anesthetized with general anesthesia.
- Three 8mm cuts are made in the upper abdomen to allow placement of three 8 mm diameter cylinders(trocars).
- A camera and two other surgical instruments are placed through these cylinders (trocars)and attached to the robotic arms.
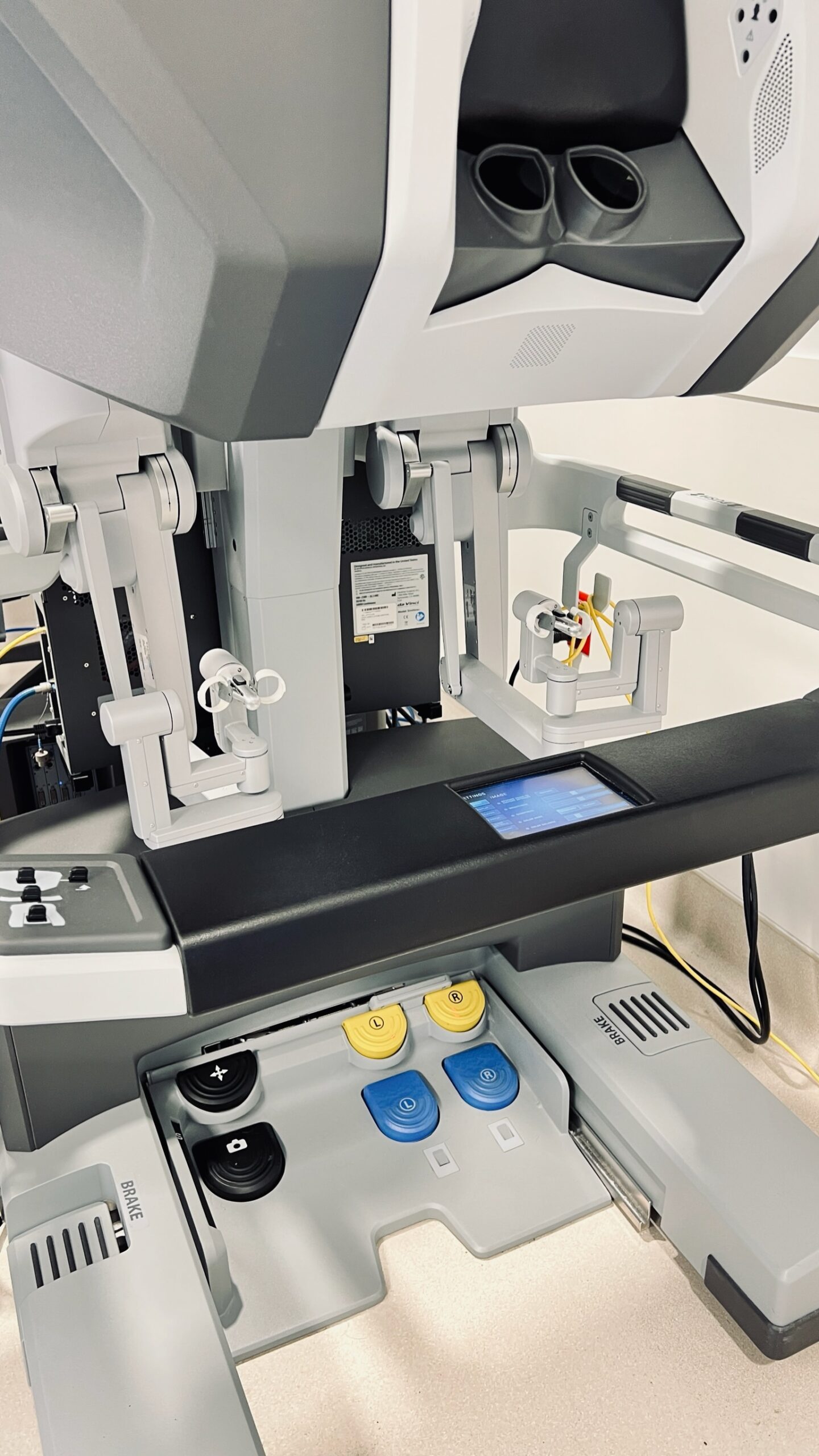
- The surgeon is sitting in a type of virtual reality console and is controlling the camera and 2 other instruments. The surgeon's hands are in a delicate controller that translates the surgeon's finger and hand movement to movement of the instruments. The instruments range from different tissue grasping devices to scissors to needle holders (used for sewing).
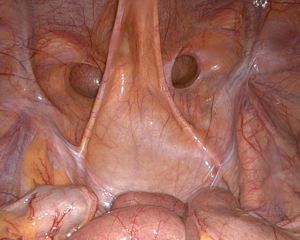
- The innermost layer (peritoneum) is delicately dissected away from the muscular abdominal wall behind the area of the hernia. The surgeon requires experience and skill in order to perform a very delicate and safe dissection. The surgeon is working in an area where many vital structures are adjacent to the area of concern for the hernia repair.
- A synthetic mesh (typically polypropylene) is placed behind the area exposed and sutured to certain key but safe locations.
- The peritoneum is sewn back to its original location as it covers the mesh within the abdominal wall.
The patient is typically discharged to home within two hours after the surgery. Most surgeons require little if any restrictions of activity during the recovery.
Less than 20% of patients will require prescription pain medicine to control their pain.
Robotic ventral hernia repair is a major improvement in outcomes compared with laparoscopic ventral hernia repair. Laparoscopic ventral hernia repair was an entirely new approach to ventral hernias compared with previous open techniques. It became more popular in the early 2000s. It allowed for repairing the hernia from the inside wall of the abdomen through 3 small abdominal incisions. The avoidance of a big incisional scar over the area of repair allows for a much lower risk of infection and wound complications compared to conventional open surgery.
Now the use of the Intuitive Davinci Robot enables
ventral hernia repair with superior visibility and robotic precision. The surgeon's visual resolution is dramatically improved with 3D ultrahigh definition inherent in the Intuitive Davinci robotic system. The surgeon is able to sit down and has much less physical stress than laparoscopy which involves standing and tiring upper extremity movements. Robotic instruments are far more precise and allow for much smoother delicate maneuvers by the surgeon.
Robotic technology allows for a much safer exposure of the hernia with a lower risk of injury to the intestine and lower risk of bleeding compared with laparoscopy. One of the biggest problems with laparoscopic ventral hernia repair is the use of multiple tacks in the abdominal wall used to fixate the mesh. Now robotic ventral hernia repair almost eliminates the need for tacks. Using the Davinci robot the surgeon is able to sew the hernia defect closed and sew a mesh to the abdominal wall with less pain than laparoscopy.
There are various techniques used in robotic ventral hernia repair. Regardless of the technique, the robot has been a game changer for patient outcomes. Robotic ventral hernia repair is typically less painful and more durable than previous laparoscopic techniques.
Robotic umbilical hernia repair is a major improvement in outcomes compared with laparoscopic umbilical hernia repair. Laparoscopic umbilical hernia repair was an entirely new approach to umbilical hernias compared with previous open techniques. It became more popular in the early 2000s. It allowed for repairing the hernia from the inside wall of the abdomen through 3 small abdominal incisions. The avoidance of a big incisional scar over the area of repair allows for a much lower risk of infection and wound complications compared to conventional open surgery.
Now the use of the Intuitive Davinci Robot enables
umbilical hernia repair with superior visibility and robotic precision. The surgeon's visual resolution is dramatically improved with 3D ultrahigh definition inherent in the Intuitive Davinci robotic system. The surgeon is able to sit down and has much less physical stress than laparoscopy which involves standing and tiring upper extremity movements. Robotic instruments are far more precise and allow for much smoother delicate maneuvers by the surgeon.
Robotic technology allows for a much safer exposure of the hernia with a lower risk of injury to the intestine and lower risk of bleeding compared with laparoscopy. One of the biggest problems with laparoscopic umbilical hernia repair is the use of multiple tacks in the abdominal wall used to fixate the mesh. Now robotic umbilical hernia repair almost eliminates the need for tacks. Using the Davinci robot the surgeon is able to sew the hernia defect closed and sew a mesh to the abdominal wall with less pain then laparoscopy.
Robotic umbilical hernia repair is typically less painful and more durable than previous laparoscopic techniques.